Copyright: Human Genome Center, Inst. Med. Sci., Univ. Tokyo; 1999-2008
Contact: Kenta Nakai |
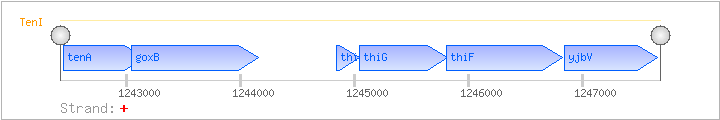
| Regulated Operon: | tenAI-goxB-thiSGF-yjbV |
| Genes | Synonyms | Direction | Genome position | Function | COG ID | Conserved groups |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tenA | + | 1242449..1243159 | COG0819K | tenA-BAC x0362-STA | ||
| tenI | + | 1243134..1243751 | COG0352H | |||
| goxB | yjbR, yjbR | + | 1243047..1244156 | glycine oxidase | ||
| thiS | yjbS | + | 1244844..1245044 | COG2104H | x0478-BAC | |
| thiG | yjbT | + | 1245041..1245811 | COG2022H | ||
| thiF | yjbU | + | 1245808..1246818 | COG0476H | ||
| yjbV | + | 1246837..1247652 | COG0351H | yjbV-BAC |
| Operon evidence: | lacZ transcriptional fusions; genome analysis |
|---|---|
| Reference: | Pang AS, et al. (1991), Mironov AS, et al. (2002) |
| Comments: | The lacZ transcriptional fusions showed that tenA and tenI belong to the same operon. Genes further downstream are assigned to this operon based on genome analysis. A terminator-antiterminator structure is found upstream of tenA. Binding of thiamin pyrophosphate to the thi-box favors transcriptional termination. |
| Binding factor |
Regulation | Location | Absolute position | Binding seq.(cis-element) | Experimental evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TenI | Negative | ND | ND | ND |
Pang AS, et al. (1991): DB |
| Terminator sequence | Absolute position | Position from stop codon | Free energy [kcal/mol] |
Downstream of |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTTATTTTACTATGCCAATTCCAAACCACTTTTCCTTGCGGGAAAGTGGTTTTTTTATTTTCAG >>>>>>>>>> <<<<<<<<<< |
tenA | |||
| TTAAATACAAGCCGATGAGATCACCAGCTGATGGTGATCTCTTTTGCGTTTGCTAC >>>>>>>>>> <<<<<<<<<< |
yjbV |
|